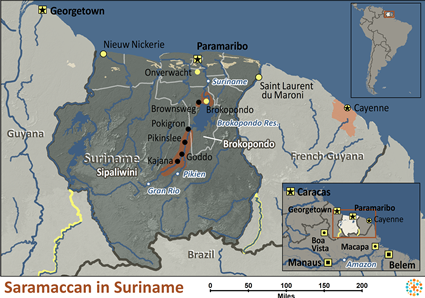
The Saramaccan or Saramaka are a people group living in the north region of South America. Most Saramaccan live in Suriname, while a smaller group resides in French Guiana.Since about the 1700s, the Saramaccan have lived near the Suriname River. They speak their own Saramaccan language. About half the Saramaccan language comes from West Africa, and the rest comes from English and Dutch.Suriname became independent from the Netherlands in 1975. During the Dutch colonial period, sugar plantations dominated the economy. Slaves from Africa provided the labor.Unfortunately, in the 1980s to 1990s, civil wars raged in Suriname as various groups contended for power. Contact with the rest of the world became difficult and living conditions deteriorated.
The Saramaccan villages are located near rivers for water, fishing, and transportation. Since the Suriname civil wars, the Saramaccan have built more western types of houses with concrete, wood, and windows in them. The Saramaccan men hunt and fish while the women do the farming. Rice is their main crop. Bananas, coconuts, and peanuts are also important cash crops. The Saramaccan now buy their clothing. Excess produce and fish are sold to buy things the Saramaccan cannot make for themselves such as cell phones and appliances.Singing, dancing, and drum playing are prominent on Saramaccan holidays.The Saramaccan often use divination or magic to determine which young people should marry. Men can have more than one wife if they can afford them. Men are only with their wives in the village for short periods of time during the year. Children are cared for by individual men or women and not by parents. Girls often marry in their teens and boys in their twenties.Village elders make judicial decisions and deal with outsiders. Saramaccans regularly use divination to get their ancestors to provide advice on major decisions.
Most Saramaccan in Suriname follow folk religion and veneration of their ancestors. Divination or fortune-telling plays a large part in their lives. This practice comes from their West African heritage. They believe in communicating with spirits and the ghosts of their ancestors. Village shamans connect the Saramaccan people with the spirit world.A tiny number of the Saramaccan are evangelical Christians.
Saramaccans need to put all their faith in Jesus Christ.
Pray that Saramaccan elders will accept the Lord and lead their people to him.Pray that God will give the Saramaccan dreams and visions, revealing to them that Jesus Christ is the way to salvation.Pray that the Saramaccan evangelicals will give their family and friends the gospel message.Ask the Lord to free the Saramaccan people from their fear of evil spirits and use of divination.
Scripture Prayers for the Saramaccan in Suriname.
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/saramakaen.wikipedia.org/wiki/Suriname
| Profile Source: Joshua Project |